Ctrl + F is the shortcut in your browser or operating system that allows you to find words or questions quickly.
Ctrl + Tab to move to the next tab to the right and Ctrl + Shift + Tab to move to the next tab to the left.
On a phone or tablet, tap the menu icon in the upper-right corner of the window; Select "Find in Page" to search a question.
Share UsSharing is Caring
It's the biggest motivation to help us to make the site better by sharing this to your friends or classmates.
Kinesiology
The study of human movement, such as anatomy, biomechanics, exercise physiology, and motor control, to understand physical performance and overall well-being.
anatomy
physiology
exercise
movement
biomechanics
muscles
bones
joints
fitness
rehabilitation
sports
kinetics
kinematics
exercise physiology
motor control
A type of force that gives impacts that are in the center causing it to bend and fold.
- Shear
- Tensile
- Compressive
Muscle Terminology: sheet or band of fibrous connective tissue that envelopes, separates, or binds together parts of the body
- Fascia
This part of long bone cover the epiphysis to a provide cushioning effect & reduce friction
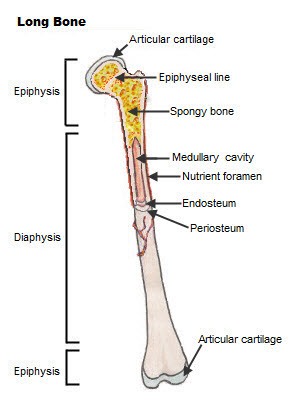
- articular cartilage
This type of contraction involves muscle developing tension to either cause or control joint movement.
- Isotonic Contraction
A type of force that causes opposing forces towards the different ends of the structure causing it to twist.
- Tensile
- Shear
- Compressive
What type of contraction is happening in the upward phase of a leg extension?
- Concentric
- Isometric
- Eccentric
You asked your client to perform elbow flexion, in gravity eliminated postion. However, but no joint motion was seen and a muscle palpatation was felt. What MMT score would you give?
- 0
- 1
- 2-
- 2+
Muscle Terminology: pertaining usually to muscles that arise or originate outside of body part upon which they actEx: Extensor digitorum"visitors"
- Extrinsic
These types of bones are small, cubical shaped, and solid bone that usually have proportionally larger articular surface in order to articulate with more than one bone.Examples include: carpals & tarsals
- Short bones
Condyle, Facet, Head
- Processes that form joints
- Processes to which ligaments, muscles, or tendons attach
- Cavities (depressions)
The definition of a Normal Soft End feel is:
- Full ROM at a joint where soft tissue stops the motion
- Full ROM at the joint where a boney structure stops the motion
- Full ROM at the joint where tendons stop the motion
- Full ROM at the joint where cartilage stops the motion
Muscles that assist in hip abduction include:
- Gluteus Maximus
- Gluteus Minimus
- Gluteus Medius
- Sartorius
- Tensor Fascia Latae
Which of the following situation is a contraindication for performing a ROM assessment?
- Patients on a pain medication
- Presence of a hematoma
- Presence of a joint inflammation
- Presence of heterotrophic ossification
If fast supination is occuring with resistance (example: when using a screw driver to tighten a screw), which additional muscles is recruited for the action of supination?
- Brachioradialis
- Biceps
- Brachialis
- Supinator
Which of the following characteristics describes the Pubofemoral ligament (check all the apply)?
- Strongest ligament
- Y shaped, with anterior and posterior portions
- Limits extension and abduction
- Limits extension and internal rotation
- Anterior fibers limit extension and external rotation, while superior fibers limit adduction
sum of muscle movement
- Aggregate
What are the three roles fulfilled by most people who work in Psychological Kinesiology? (choose all the correct answers)
- researching
- researching
- training
- teaching
- directing
- practicing
The mechanism of how the force was applied is just as important as its ______________________.
- impact
Kiinsiology is related to ?
- study of human bones
- study of history
- study of human movements
- study of healthy habits
These measures aim to capture information that cannot be attained through behavioral or self-report measures alone.
- psychophysiology
A Sport Psychology Consultant is legally allowed to treat mental health issues.
- True
- False
What is the Prime Mover during a Leg Extension?
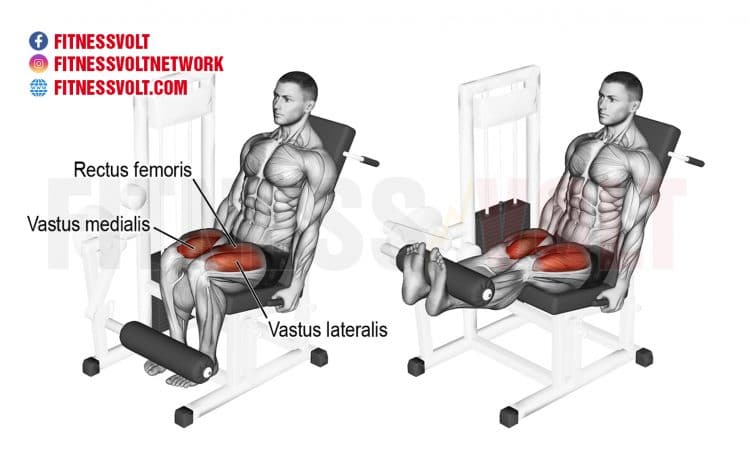
- Quadricep
- Hamstring
- Iliopsoas
- Gluteal
There are 4 properties of muscles that relate to its ability to produce force and effect movement. Which property is being described: - ability of muscle to contract and develop tension or internal force against resistance
- Contractility
Fibers run obliquely from a tendon on one side onlyEx: Biceps femoris
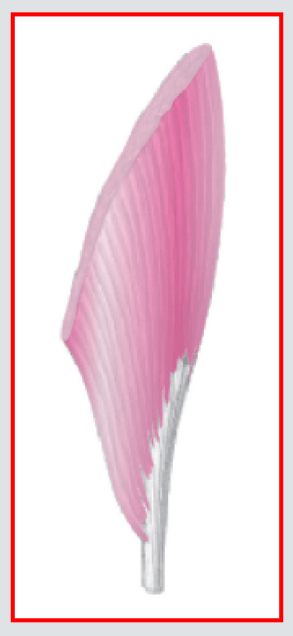
- Unipennate
factors in to a muscle's ability to move through a wide range of motion.
- Length of muscle and ability to shorten
Circular muscles; technically endless strap muscles that surround opening and function to close them upon contraction. Ex: orbicularis oris

- Sphincter Muscles
Articular cartilage is the thickest where?
- Inside the acetabulum
- Head of the femur
- Neck of the femur
- On the rim of acetabulum
- All of the above
Fibers run obliquely on both sides from a central tendon.Ex: rectus femoris

- Bipennate
The definition of a Normal Hard End feel is:
- Full ROM at a joint where soft tissue stops the motion
- Full ROM at the joint where a boney structure stops the motion
- Full ROM at the joint where tendons stop the motion
- Full ROM at the joint where cartilage stops the motion
It's important that Psychological Kinesiologists who primarily work in the area of Practice use science and evidence and participate in research to further the field.
- True
- False
There are 4 properties of muscles that relate to its ability to produce force and effect movement. Which property is being described: - ability of muscle to return to its original resting length after stretching
- Elasticity
This plane divides the body into right and left.
- Sagittal
- Transverse
- Frontal
Mechanical effects of coxa valgus and coxa vara include all of the following except:
- Altered muscle moment arm
- Altered joint reaction force alignment
- Altered arrangement of cancellous bone arrays
- Decreased stabilty of the hip joint
- All of the above are mechanical effects
Flexion is _______
- An increase in joint angle
- A decrease in joint angle
- Movement away from midline
- Movement towards midline
Also described sometimes as being triangular, fan shaped or convergent. Originate on broad aponeuroses and converge onto a tendon. Ex: pec, trap

- Radiate Muscles
A musculoskeletal structure that provides movement to the body.
- Joints
- Ligaments
- Muscles
- Bones
If slow supination is occuring without resistance (example: positioning your hand in a palms up position to recieve change from the cashier), which muscle of the forarm is most active?
- Brachioradialis
- Biceps
- Brachialis
- Supinator
Exercise Psychology research is thought to have been driven by this:
- NFL football
- Tour de France
- the "Fitness Craze"
The two joints in play during a Lat Pull Down are the
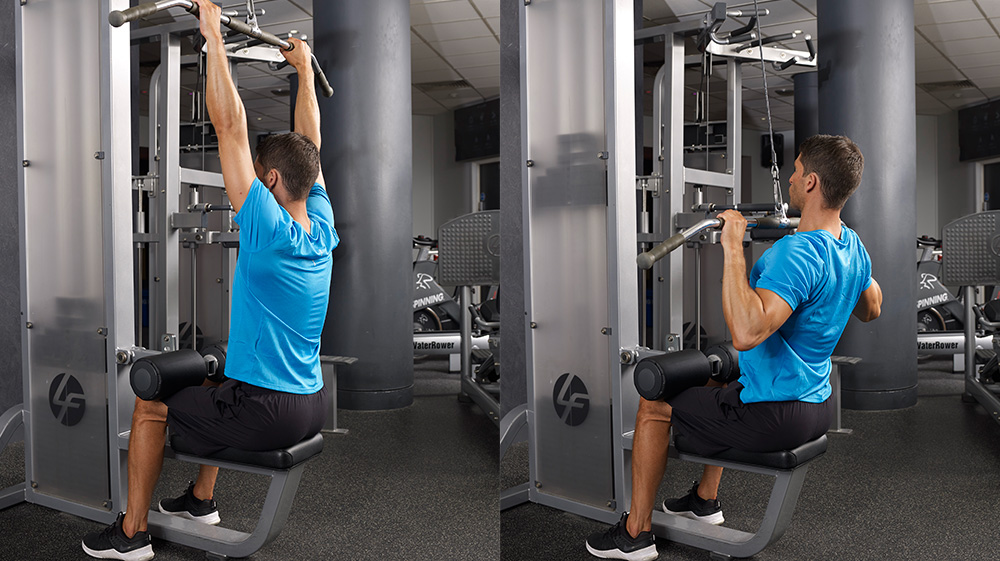

- Elbow and Shoulder
The musculoskeletal structure that attaches the bone to the muscle
- Joints
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Muscles
The joint capsule of the hip.....
- Surrounds the acetabulum
- Surrounds the acetabulum
- Attaches to the greater and lesser trochanters
- Encloses the femoral head and most of the neck
- Attaches to the intertrochanteric line and crest
The primary blood supply to the femoral head comes from where?
- Femoral artery
- Neck of the femur
- Arterioles surrounding the head of the femur
- Femoral vein
- Sciatic nerve
Position of the hip is dependant on which of the following?
- Pelvis
- Femur
- Muscles of the pelvis
- Ligaments
- Articular cartilage
All stimuli induce a gut response of "pleasant" or "unpleasant" that is immediate and subconscious. What is this gut response called? (2 words)
- Basic Affect
These type of fibers are arranged parallel to length of the muscle; generally produce a wider ROM.Ex: flat, fusiform, strap, radiate, sphincter
- Parallel
Acetabulum is formed by what structures?
- Ilium
- Ilium
- Ischium
- Femor
- Pubis
Facet, Foramen, Fossa, Fovea, Meatus, Notch, Sinus, and Sulcus
- Processes that form joints
- Processes to which ligaments, muscles, or tendons attach
- Cavities (depressions)
A musculoskeletal structure that stabilizes the joint.
- Joint
- Bone
- Muscles
- Ligaments
Which joint action occurs when the spine bends sideways?
- Adduction
- Horizontal extension
- Lateral flexion
- Rotation
The floor of the hip joint is ...
- Thin and nonarticular
- Thick and articular
- Thin and articular
- Thick and nonarticular
- None of the above
What are some of the sub-disciplines of Sport Psychology? choose all the correct answers.
- Biology
- Behavioral change and interventions
- Biochemistry
- Motor Behavior
What is the joint action in the downward phase of a Tricep Dip?
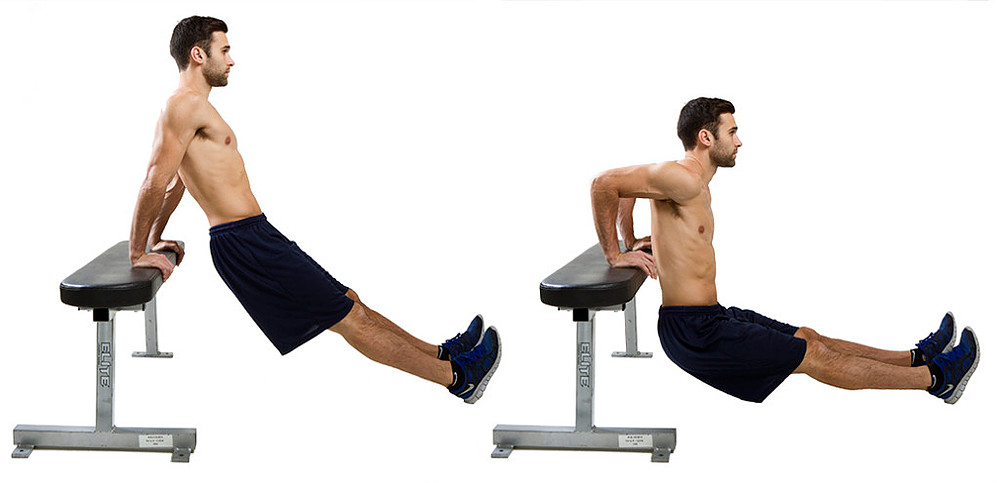

- Elbow Extension
- Elbow Flexion
Skeletal muscles are responsible for movement of the body and all its joints. What are the other functions?
- Dynamic Stability of joints
- Dynamic Stability of joints
- Protection of joints
- Protection of vital organs
- Produce a major portion of body heat
What type of muscle contraction is happening during the downward phase of a tricep dip?
- Concentric
- Eccentric
More uniform in diameter with essentially all fibers arranged in a long parallel manner. Enables a focusing of power onto small, bony targets.Ex: Sartorius
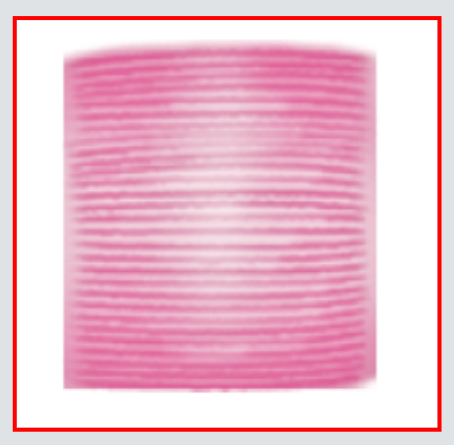

- Strap Muscles
A Prime mover can be described as
- The opposing muscle to the agonist
- The muscle that causes a desired action
- The muscle that stabilizes a part of the body
- The muscle that assists a movement
When performing muscle strength testing on the brachialis muscle, how should you position the forearm?
- Forearm should be positioned in supination
- Forearm should be positioned in pronation
- Forearm should be positioned in mid-position
- Forearm position does not matter
The hip joint is (check all that apply)...
- Triaxial
- Triaxial
- Ball and socket
- Synovial
In order to earn the AASP's Certified Mental Performance Consultant credential, you must complete the following: (choose all the correct answers)
- complete a master's or doctorate degree related to sport psychology
- complete a master's or doctorate degree related to sport psychology
- pass an exam
- take a specific set of graduate courses
- complete 400 hours of supervised practice in sport psychology
Muscle Terminology: specific movement of joint resulting from a CONCENTRIC CONTRACTION of a muscle which crosses jointEx: biceps action is elbow flexion, radioulnar supination
- Action
The socket of the acetabulum faces what directions?
- Medially, slightly inferior, and anteriorly
- Medially, slightly superior, and posteriorly
- Laterally, slightly superior, and posteriorly
- Laterally, slightly inferior, and anteriorly
- Laterally, slightly inferior, and posteriorly
___ pairs of muscles work in cooperation with one another to perform opposite actions at the joints they cross.
- 315
- 300
- 215
- 200
Muscle Terminology: pertaining to muscles within or belonging solely to body part upon which they actEx: Lumbricals"Locals"
- Intrinsic
Psychological kinesiology is an umbrella term for the study of human movement that encompasses one's _____________.
- psyche
Surveys can be used to test theories.
- True
- False
Norm Triplett, an early social psychologist to whom the origin of research and academics in sport and exercise psychology is traced back to, tested his hypothesis with children and what task?
- throwing a baseball
- reeling in a fishing line
- jumping on a trampoline
- doing jumping jacks
Bones that are pushed out from their joint capsule are called ________.
- DISLOCATION
Role of Muscles: assist in the action of an agonist but are not necessarily prime movers of the action.- guiding muscles - assist in refined movement - rule out undesired motion
- Synergists
Longer the lever, greater the.............
- Strength
This part of long bone is the dense, fibrous membrane covering the outer surface of the diaphysis

- periosteum
All of the following functions of the brachioradialis muscle are correct EXCEPT:
- The brachioradialis muscle can function as an elbow joint stabilizer
- The angle of pull of the brachioradialis muscle allows for joint approximation
- The brachioradialis muscle operates as a force in a third-class lever system
- The brachioradialis muscle operates as a force in a second-class lever system
Muscle Terminology: segment of nervous system responsible for providing a stimulus to muscle fibers within a specific muscle or portion of a muscle.- a muscle may be innervated by more than one nerve and a particular nerve may innervate more than one muscle or portion of a muscle
- Innervation
Osteoarthritis is an example of what type of injury?
- Overuse Injury
Tissues and Fats has the capacity to lessen the impact of force.
- True
- False
Muscle Terminology: tendinous expansion of dense fibrous connective tissue that is sheet or ribbon like, resembling a flattened tendon, serve as fascia to bind muscles together
- Aponeurosis
The weakness of hip abductors causes:
- Decreased abduction
- Decreased abduction
- Decreased adduction
- Instability during single leg stance
- Glut medius limp
Edric was trying to reach the light bulb when he lost his balance and sprained his ankle. Due to the circumstance that he was alone during that time, it took 30 minutes before help came. While he was inside the ambulance, the paramedics notice that Edric could no longer feel and move his ankle. What category of damaged tissue is he suffering from?
- Mild
- Moderate
- Severe
which law of motion is working in this image.
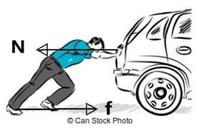
- [No Answer]
Which of the following is an origin of the triceps brachii
- Radius
- Sternum
- Ulna
- Humerus
Vernon who suffered from a sprain only feels pain on his ankle when its moved. From this, what category of damaged tissue is he suffering from?
- Mild
- Moderate
- Severe
Lifting phase of the squat:
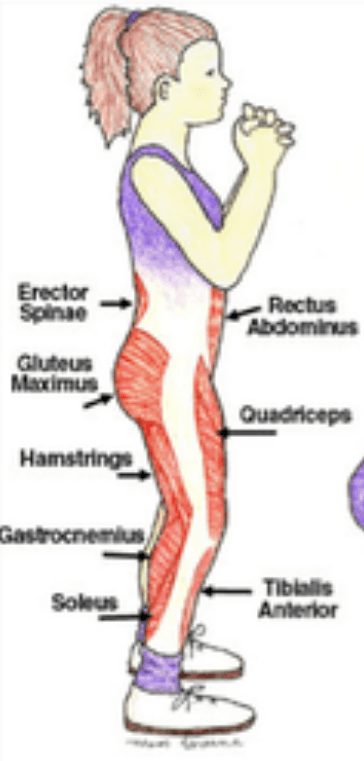
- Concentric Contraction
- Eccentric Contraction
Ligaments of the hip joint provide which of the following functions?
- Limit hyperextension ROM and reinforce anterior capsule
- Limit ROM in all directions and reinforce anterior capsule
- Limit hyperextension ROM and reinforce posterior capsule
- Limit ROM in all directions and reinforce posterior capsule
- Limits hyperextension only
This plane of motion divides the body into front and back.
- Transverse
- Frontal
- Sagittal
Minimum length of the pronator teres occurs in which of the following joint positions:
- Full elbow extension, full forearm supination, position of shoulder is inconsequential
- Full elbow flexion, full forearm pronation, positon of shoulder is inconsequential
- Full elbow flexion, full forearm supination, full shoulder flexion
- Full elbow extension, full forearm pronation, full shoulder extension
Which of the following characteristics describe the Iliofemoral ligament (check all the apply)?
- Strongest ligament
- Strongest ligament
- Y shaped, with anterior and posterior portions
- Limits extension and abduction
- Limits extension and internal rotation
- Anterior fibers limit extension and external rotation, while superior fibers limit adduction
What is the mechanism of injury in tennis elbow?
- Inflammation of biceps tendon at the head of the radius due to repeated and forceful elbow flexion
- Inflammation of the biceps tendon at the superior humeroradial joint due to repeated and forceful elbow flexion
- Inflammtion of the triceps tendon at the olecranon process due to repeated and forceful elbow extension
- Inflammation of the wrist extensors or wrist flexors at their origins (medial epidcondyle for wrist flexors; lateral epicondyle for wrist extensors) due to repeated forceful action of wrist extensors or wrist flexion
Have several tendons with fibers running diagonally between them.Ex: deltoid

- Multipennate
Overall congruence of the hip joint does what to the femroal head and acetabulum?
- Decreases stress between femoral head and acetabulum
- Decreases stress between femoral head and acetabulum
- Allows for the joint to follow the convex-concave rule
- Increases forces between femoral head and acetabulum
- Increases stability
Role of Muscles: Surrounds joint or body part. Contract to fixate the area to enable another limb or body segment to exert force and more.
- Stabilizers
Hip flexors include which of the following one joint muscles?
- Psoas Major and Minor
- Psoas Major and Minor
- Iliacus
Muscle Terminology: distal attachment of a muscle. Functionally and historically the most movable part.
- Insertion
Newton's Second Law of motion is related to
- Speed
- Acceleration
- opposite reaction
- Momentum
Extension takes place in the __________ plane.
- Sagittal
- Frontal
- Transverse
What joint action occurs in the upward phase of a calf raise?
- Dorsiflexion
- Protraction
- Plantarflexion
Muscle Terminology: central, fleshy portion of the muscle; increases in diameter as a muscle contracts
- Gastor
What are some differences in the hip joint from the shoulder joint?
- Hip is more stable and less mobile than shoulder joint
- Shoulder joint has more stability from muscles than hip joint
- Hip joint is more congruent than the shoulder joint
- All of the above are differences
- None of the above are differences
A musculoskeletal structure that serves as the fulcrum of movement.
- Joints
- Tendons
- Bones
- Muscles
Engaging with psychological kinesiology is acknowledging the importance of the ___________ ____________ in physical activity, exercise, and sport. (two words)
- human element
factors in to a muscle's ability to exert force
- cross sectional diameter
Flexion takes place in the ____________ plane.
- Frontal
- Transverse
- Sagittal
The initials of the main organization for modern psychological kinesiology are:
- NASPSPA
- ACSM
- APA
- AASP
A wound is an example of what type of injury?
- Acute Injury
What is the Prime Mover during a calf raise?
- Gastrocnemius/Soleus
- Tibialis
- Hamstring
- Quadricep
Muscles that assist in internal rotations include:
- Medial Hamstrings
- Medial Hamstrings
- Sartorius
- Tensor Fascia Latae
There are 4 properties of muscles that relate to its ability to produce force and effect movement. Which property is being described: - ability of muscle to be passively stretched beyond its normal resting length
- extensibility
What is the Prime Mover in a sit up?
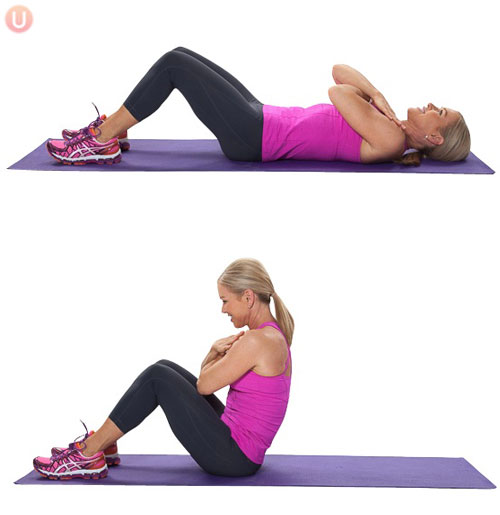

- Rectus Abdominis
- Erector Spinae
- Quadriceps
- Latissimus dorsi
A tissue can only be damaged when it receives an impact stronger than what it can absorbed.
- True
- False
Which theory is described by this statement: "Intentions are considered the primary drive of human behavior."
- Self-Determination Theory
- Theory of Planned Behavior
- Health Belief Model
- Trans-Theoretical Model of Behavior Change
The two joints involved in a Dumbbell Chest Press are the

- Elbow and shoulder
Primary hip abductors include which of the following?
- Gluteus Maximus
- Gluteus Minimus
- Gluteus Medius
A sprain and strain are examples of what type of injury?
- Acute
This part of long bone is the growth plate or the thin cartilage that separates the diaphysis & epiphyses

- Epiphyseal plate
Abduction takes place in the ____________ plane.
- Frontal
- Sagittal
- Transverse
An example of an Abnormal End feel that is SOFT is:
- Decreased ROM at a joint where cartilage stops the motion
- Decreased ROM at a joint where joint edema stops the motion
- Decreased ROM at a joint where pain stops the motion
- Decreased ROM at a joint where a ligament stops the motion
The scientific study of human movement.
- Kinematics
- Kinesiology
- Kinetics
Abduction mean to ____________
- Move towards midline
- Increase the joint angle
- Move away from midline
- Decrease the joint angle
Lateral rotation takes place in the ___________ plane of motion.
- Sagittal
- Frontal
- Mid Saggital
- Transverse
The stabiltiy of the hip joint is provided by what?
- Bony surfaces
- Strong ligaments
- Muscles that surround the joint
- Both bony surfaces and strong ligaments
- Bony surfaces, strong ligaments, and muscles that surround the hip joint
Minimal length of the Biceps occurs in which of the following joint positions:
- Full shoulder extension, full elbow flexion, full forearm pronation
- Full shoulder flexion, full elbow flexion, full forearm supination
- Full shoulder flexion, full elbow extension, full forearm supination
- Full shoulder extension, full elbow extension, full forearm pronation
Role of Muscles: muscles that, when contracting concentrically, cause joint motion
- Agonists
These types of bones usually have a curved surface & vary from thick where tendons attach to very thin. Examples include: ilium, ribs, sternum, clavicle, & scapula
- flat bones
What joint action is happening in the upward phase of a Back Extension
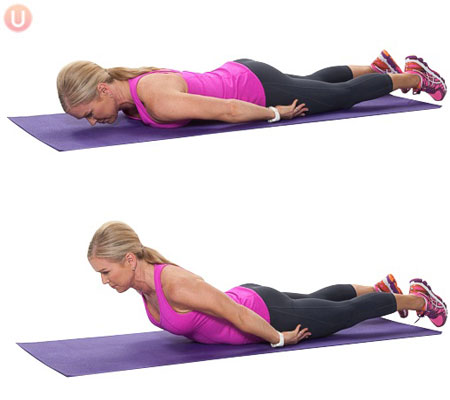

- Spine hyperextension
- Spine protraction
- Spine Flexion
The weakness of adductor muscles causes:
- Is caused by injury to Obturator N
- Is caused by injury to Obturator N
- Is not common
What type of contraction is happening in the quads during the upward phase of the squat
- Eccentric
- Isometric
- Concentric
Walking typically uses how much hip flexion?
- 10-20 degrees
- 20-30 degrees
- 30-40 degrees
- 40-50 degrees
- 50-60 degrees
Historically, psychology emerged as a field of science/investigation and practice operating from the ____________ model, looking for what is "wrong" with someone and then alleviating the symptoms.
- deficit
One joint hip adductors include:
- Gracilis
- Pectineus
- Adductor Brevis
- Adductor Longus
- Adductor Magnus
Which of the following describes the documentation of elbow ROM as 30 degrees- 105 degrees
- Pt. has -105 degrees of elbow flexion
- Pt. has -30 degrees of elbow extension
- Pt. can fully flex elbow
- Pt. can fully extend elbow
Your client demonstrates full agaisnt gravity ROM of elbow flexion and can take moderated resistance. What MMT score would you give?
- 5
- 4
- 4-
- 3+
Tissues can't withstand varying degrees of stress and strain.
- True
- False
Increased tightness in hip flexors cause:
- Decrease hip flexion
- Decrease hip extension
- Anterior pelvic tilt in standing, causing lumbar lordosis
The examination of and practices associated with helping people optimize their relationships, their work, and their general activities and engagement with the social and physical world is often called:
- expert study
- talent education
- positive psychology
- exercise psychology
Functions of the elbow complex include all of the following EXCEPT:
- The rotation at the elbow complex allows for orientation of the hand during activities
- The elbow provides stability during UE weight-bearing activities
- Muscle movement of the elbow is functionally independent from movement of the shoulder or wrist
- The elbow provides mobility of the hand in space by lengthening and shortening the UE
Adduction takes place in the __________ plane.
- Frontal
- Transverse
- Sagittal
What is the difference between coxa valga and coxa vara?
- Coxa valga descrives excessive femoral neck angle and coxa vara describes normal femoral neck angle.
- Coxa valga describes excessive femoral neck angle and coxa vara describes a lack in femoral neck angle
- Coxa valga describes normal femoral neck angle and coxa vara describes excessive femoral neck angle
- Coxa valga describes normal femoral neck angle and coxa vera describes a lack in femoral neck angle
- Coxa valga describes a lack in femoral neck angle and coxa vara describes excessive femroal neck angle
This part of long bone is the ends of the long bone and is formed from cancelleous (spongy or trabecular) bone.

- Epiphysis
One joint hip extensors include which of the following?
- Quads
- Hamstrings
- Gluteus maximus
- Gluteus Minimus
- Adductor magnus
What is the prime mover during hip extension of a squat?
- Hamstrings
- Gluteals
- Iliopsoas
- Quadriceps
A type of force that acts away from the center of the structure, causing a pull or stretch.
- Tensile
- Compressive
- Shear
These types of fibers are shorter fibers that are arranged obliquely to their tendons; similar structure to a feather; generally have a wider cross section and therefore more force production capability.
- Pennate
There are 4 properties of muscles that relate to its ability to produce force and effect movement. Which property is being described: - sensitive or responsive to chemical (change in axons), electrical, or mechanical stimuli.
- Irritability/Excitability
The joint action during the downward phase of the Lat pull down is
- Shoulder adduction and flexion
- Shoulder abduction and extension
What is the normal femoral neck angle?
- 15 degress
- 45 degrees
- 90 degrees
- 125 degress
- 150 degress
•During acute injuries, the body will initiate the healing process through the ___________________.
- Swelling Response
- Bruising Response
- Inflammatory Response
- Immediate Response
Spindle-shaped with a central belly that tapers to tendons on each end. Allows them to focus their power onto small, bony targets.Ex: Brachialis
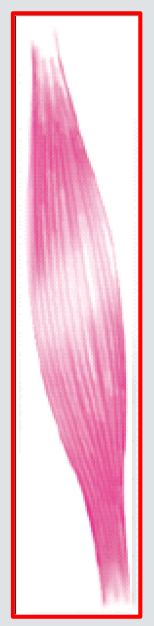
- Fusiform Muscles
Human behavior exists on a continuum.
- True
- False
The hip joint is deepened by which structure?
- Ligaments
- Muscles of the hip
- Acetabulum
- Femur
- Labrum
This part of long bone is the hard, dense compact bone that form the walls of the diaphysis

- cortex
The tightness of hip extensors causes:
- Decreaed hip extension
- Decreased hip flexion
- Decreased external rotation
- Decreased internal rotation
- Lower back pain
Large bending moments in the neck of the femur are sustained by what?
- Articular cartilage
- Ligaments
- Joint capsule
- Trabecular bone
- Calcaneous bone
Achilles Tendinitis is an example of what type of injury?
- Overuse Injury
Maximal length of the Triceps occurs in which of the following joint positions:
- Full shoulder extension, full elbow extension, position of forearm is inconsequential
- Full shoulder flexion, full elbow flexion, position of forearm is inconsequential
- Full shoulder extension, full elbow flexion, full forearm pronation
- Full shoulder flexion, full elbow extension, full forearm supination
An example of an Abnormal End feel that is EMPTY is:
- Decreased ROM at a joint where cartilage stops the motion
- Decreased ROM at a joint where joint edema stops the motion
- Decreased ROM at a joint where pain stops the motion
- Decreased ROM at a joint where a ligament stops the motion
Fractures and dislocations are injuries that are life-threatening.
- True
- False
Two situations in which completion of MMT assessment is contraindicated are:
- Patient is on pain medication and is fatigued
- Patient has joint pain and inflammation
- Patient has hypertension and diabetes
- Patient has joint hypermobility and COPD
The weakness of hip extensors causes:
- Decreased hip extension
- Decreased hip extension
- Decreased hip flexion
- Lurch when wallking
This type of contraction takes place when muscle lengthens under tension. It also occurs when muscle gradually lessens in tension to control the descent of resistance. Controls movement with gravity or resistance.- "negative contraction"
- Eccentric Contraction
Usually thin and broad, originating from broad, fibrous, sheet-like aponeuroses. Allows them to spread their forces over a broad area.Ex: Rectus abdominus

- Flat Muscles
Tightness in hip abduction causes:
- Decreased hip abduction
- Decreased hip adduction
- Pelvic drop during standing
Roles of Muscles: muscles that have the opposite concentric action from antagonists.- Located on the opposite side of the joint as the agonists- Work cooperatively with agonist muscles to by relaxing and allowing movement
- Antagonists
Lowering phase of the squat:
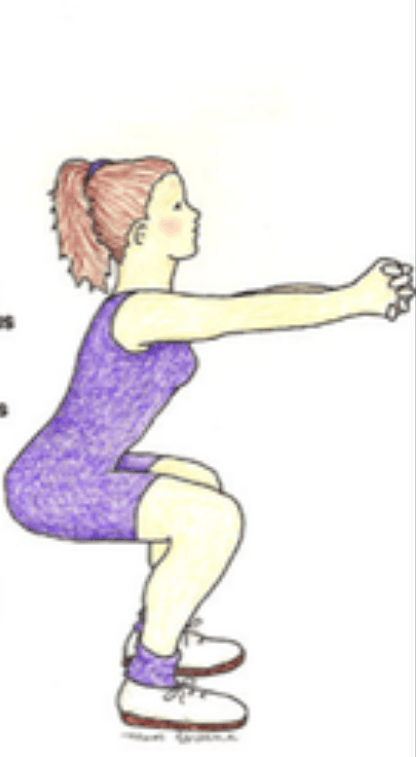
- Concentric Contraction
- Eccentric Contraction
In what direction does the femoral head face?
- Medially and anteriorly
- Laterally and posteriorly
- Superiorly and medially
- Superiorly and anteriorly
- Medially and posteriorly
This type of contraction takes place when muscle develops tension as it shortens. It also occurs when muscle develops enough force to overcome applied resistance and causes movement against gravity or resistance.- "positive contraction"
- Concentric Contraction
The ligament to the head of the femur
- Provides mechanical support and blood supply to femoral head
- Provides stabilization and limits hip extension
- Provides little mechanical support and helps stabilize the hip joint
- Provides lirrle mechanical support and inadequate blood supply to femoral head
- Provides stabilization and inadeqaute blood supply to femoral head
The prime mover in the upward phase of shoulder flexion in a dumbbell chest press?
- Bicep
- Tricep
- Pectorals
- Trapezius
Sport Psychology is a science.
- True
- False
IF a paitent is able to move a joint in full active range of motion against gravity, what number grade is automatically given, before applying resistance?
- 3
- 3+
- 2+
- 3-
One of the most consistent psychological concepts that relates to successful outcomes in both sport and exercise. (two words or a hyphenated word.)
- self-efficacy
Kinesiology is the study of _______________.
- How the body works
- How the body moves
- Origins and Insertions
- Disease and Illness
This type of contraction takes place when tension is developed within muscle but joint angles remain constant (no movement).
- Isometric Contraction
The TWO joints that come into play during a squat are the
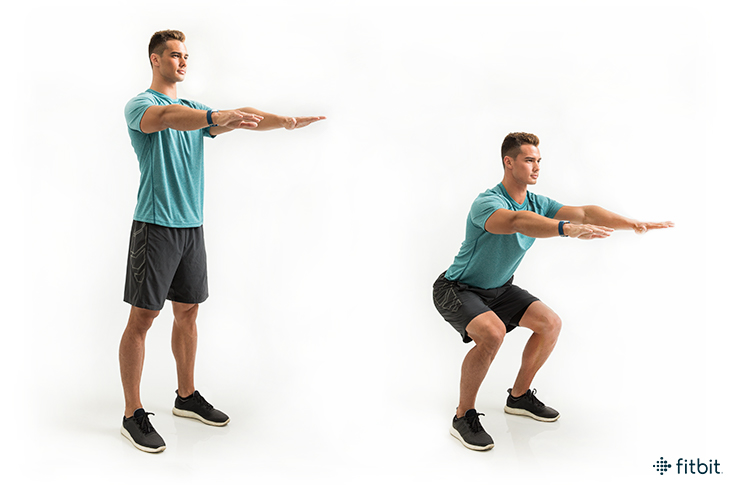

- Hip and the Knee
Which of the following are two joint hip flexors?
- Psoas Major and Minor
- Iliacus
- Rectus Femoris
- Tensor Fascia Latae
- Sartorius
Which of the following is a type of connective tissue that helps form the joint capsule?
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Muscles
- Labrum
- Synovial fluid
The tightness of adductor muscles:
- Is not common
- Causes decreased swing leg or step length during gait
- Due to injury to Obturator N
- Causes low back pain
- Has no significant implications
What structure of the hip limit ROM?
- Ligaments
- Muscles
- Bony structures (acetabulum and femoral head)
- A and B are correct
- A and C are correct
Which statement is correct about ROM and MMT assessment?
- MMT should be assessed before ROM to determine muscle strength in order to understand joint integrity
- MMT should be assessed before ROM to determine how much mobility is available in the joint in order to understand muscle strength
- ROM should be assessed before MMT to determine muscle strength and muscle contraction in order to understand joint function
- ROM should be assessed before MMT to determine the amount of joint mobility and joint integrity in order to understand muscle strength
Which of the following statements is NOT true about the differences between AROM and PROM:
- AROM is always larger than PROM because of muscle contraction
- A decrease in PROM and AROM of a joint may be due to joint contracture
- If PROM is WNL but AROM is limited, muscle strength may be the limiting factor
- PROM is equal to or larger than AROM because of stretch of soft tissues and relaxed muscles
___ skeletal muscle, constitute approx. 40-50% of our body weights.
- 700
- 600
- 500
- 400
What is the joint action during the downward phase of a leg extension?
- Hip Flexion
- Hip Extension
- Hip Adduction
- Hip Abduction
Weak hip flexors cause:
- Decreased hip extension
- Decreased hip flexion
- Decreased hip abduction
- Decreased hip adduction
- Decreased hip rotation
The articular surface of the hip joint is located where?
- On the inferior surface
- Along the rim
- Along the head of the femur
- On the posterior surface
- Along the medial and lateral sides of the joint capsule
What joint action is happening in the upward phase of the sit up?
- Spine Extension
- Spine Flexion
- Spinal rotation
- Spinal retraction
The type of contraction during the upward phase of a Lat pulldown
- Eccentric
- Concentric
Which of the following is a situation in which the therapist should proceed with caution when measuring ROM?
- No limitations with occupational performance
- Unhealed fracture
- Joint dislocation
- Inflammatory process in joint
Ratio between the diameter of the acetabulum and depth is lowest when?
- At birth
- Puberity
- After skeletal maturity (early-mid 20s)
- After age 40
- After age 65
A type of injury that occurs after a long period of exposure of the force.
- Chronic Injury
Which of the following characteristics describes the Ischialfemoral ligament (check all the apply)?
- Strongest ligament
- Y shaped, with anterior and posterior portions
- Limits extension and abduction
- Limits extension and internal rotation
- Anterior fibers limit extension and external rotation, while superior fibers limit adduction
External Rotators of the hip include:
- Piriformis
- Piriformis
- Obturators
- Quadratus femoris
- Gemellis superior and inferior
These types of bones have a long cylindrical shaft with relatively wide, protruding ends. Examples include: phalanges, metatarsals, metacarpals, tibia, fibula, femur, radius ulna, & humerus
- long bones
The Prime Mover in the upward phase of elbow extension in a Dumbbell Chest Press?
- Biceps
- Triceps
- Trapezius
The original model of Trans-Theoretical Behavior Change proposed how many stages?
- 5
This part of long bone is the long cylindrical shaft

- diaphysis
Normal transverse plain alignment includes:
- Slight anteversion of 25 degrees
- Slight anteversion of 20 degrees
- Slight anteversion of 15 degrees
- Slight anteversion of 10 degress
- Slight anteversion of 5 degrees
What makes the head of the femur more spherical?
- Hyaline cartilage
- Articular cartilage
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Acetabulum
Which of the following describes the shape of the head of the femur?
- Complete sphere
- 1/3 sphere
- 2/3 sphere
- Cylindrical
- Ball
This part of long bone is between the walls of the diaphysis, containing yellow or fatty marrow.

- medullary cavity
These types of bones are small bones embedded within tendons of a musculotendinous unit that provide protection as well as improve the mechanical advantage. Examples include: patella, flexor tendons of great toe and thumb
- sesamoid bone
Sprain is to bruising; strain is to __________.
- swelling
- muscle spasms
- bleeding
- blood clotting
Muscle Terminology: proximal attachment of a muscle. Functionally and historically the least movable part.
- origin
The definition of a Normal Firm End feel is:
- Full ROM at a joint where soft tissue stops the motion
- Full ROM at the joint where a boney structure stops the motion
- Full ROM at the joint where tendons stop the motion
- Full ROM at the joint where cartilage stops the motion
Two joint hip extensors include which of the following?
- Quads
- Hamstrings
- Gluteus Maximus
- Gluteus Minimus
- Adductor Magnus
Why is elbow positioning critical for optimal function of the extrinsic muscles of the hand? What is the optimal position of the elbow for extrinsic hand function?
- Because extrensic muscles insert distal to the elbow joint, elbow position can impact the length tension relationship of the extrinsic muscles. Elbow flexion at 100 degrees is optimal position.
- Because extrinsic muscles of the hand do not cross the elbow joint, elbow position is not critical
- Because extrinsic muscles of the hand do not cross the elbow joint, elbow position can impact the length tension relationships of the extrinsic muscles. Elbow flexion at 75 degrees is optimal position.
- Because extrinsic muscles of the hand cross the elbow joint, elbow position can impact length tension relationships of extrinsic muscles. Elbow flexion at 90 degrees is optimal position.
Exercise Psychology investigates the influences of one's psyche towards ___________ as well as how ____________ influences one's psyche. (same answer for both blanks)
- fitness
- wellness
- exercise
- cardio
A concentric contraction can be described as
- A muscle that generates force and lengthens
- Muscle actions involving movement at a constant speed
- A muscle that generates force and stays the same length
- A muscle that generates force and shortens
Should MMT be performed with the joint in closed packed position or an open packed position? WHY?
- MMT should be performed with the joint in open packed position so that the client can stabilize joint using joint soft tissue and/or boney structures
- MMT should be performed with the joint in closed packed position so that the client can stabilize the joint using joint soft tissue and/or boney structures
- MMT should be performed wit the joint in open packed position so that the client uses muscles and not joint soft tissue and/or boney structures to stabilize the joint
- MMT should be performed with the joint in closed packed position so that the client uses muscles and not joint soft tissues and/or boney structures to stabilize the joint
Valgus and anteversion
- Change during development
- Never change
- Change in indication of pathological damage to the hip joint
Normal hip ROM.
- Depends on age
- Does not vary
- Gender has small effect on
The bicep does elbow flexion. The opposite motion is elbow extension. Therefore, what is the antagonist to the bicep muscle?
- Triceps
Tibial torsion and foot alignment are affected by
- Frontal plane alignment
- Sagittal plane alignment
- Transverse plane alignment
- None of the above
- All of the above
In our institution, who get the Vikram Award in Basketball ?
- Image: https://quizizz.com/media/resource/gs/quizizz-media/quizzes/1e0f11a8-88bd-4b5e-a142-5593f589b167?w=90&h=90
- Image: https://quizizz.com/media/resource/gs/quizizz-media/quizzes/9bbd2c16-3f62-4794-adf6-566c7d28278f?w=90&h=90
- Image: https://quizizz.com/media/resource/gs/quizizz-media/quizzes/40843ac5-2b20-4625-a4f6-5abe4c09c04c?w=90&h=90
- Image: https://quizizz.com/media/resource/gs/quizizz-media/quizzes/f4f0bd01-ed54-4d43-ae9a-eb342de3334f?w=90&h=90
Muscle Terminology: tough yet flexible bands of fibrous connective tissue, often cord like in appearance, connect muscles to bones and other structures
- Tendon
Two joint muscles in hip adduction include:
- Gracilis
- Adductor Brevis
- Adductor Longus
- Adductor Magnus
- Pectineus
Normal hip motion is linked to:
- Pelvic motion
- Pelvic motion
- Low back motion
When applying resistance during a MMT, should you place your hand proximal or distal the joint of the muscle being tested? WHY?
- Your hand needs to be placed on the distal end of the bone that is being moved by the muscle bc you have better mechanical advantage
- Your hand needs to be placed on the proximal end of the bone that is being moved by the muscle bc you can eliminate muscle subsitutions
- Your hand needs to be placed on the proximal end of the bone that is being moved by the muscle bc you have better mechanical advantage
- Your hand needs to be placed on the distal end of the bone that is being moved by the muscle bc you will be able to palpate the muscle
You are doing ROM and MMT assessment of shoulder flexion of a patient. The patient demonstrates full PROM of shoulder flexion. However, during AROM against gravity, patient can only flex shoulder from 0-100 degrees. Which of the following interpretation is correct:
- You should retest AROM of shoulder flexion using moderated resistance
- Patient has mechanical shoulder joint issues
- You can give the patient a MMT grade of 3- for shoulder flexion
- You can give the patient a muscle grade of 3 for shoulder flexion
Muscle Terminology: when tension is developed in a muscle as a result of a stimulus
- contraction
ARE BREAKS IN THE CONTINUITY OF THE BONE.
- FRACTURE
Paddy Ekkekakis and Steven Petruzzello noted that the post-exercise measures of mood/emotional state more likely captured a ___________ effect. People indicated feeling good (better than baseline) only because a potentially aversive stimulus (physical exertion) had recently been removed.
- rebound
What is the antagonist muscle during a calf raise?

- Gastrocnemius
- Tibialis
- Hamstring
Crest, Epicondyle, Line, Process, Spine (spinous process), Suture, Trochanter, Tubercle, and Tuberosity
- Processes that form joints
- Processes to which ligaments, muscles, or tendons attach
- Cavities (depressions)
Your client demonstrates against gravity ROM of shoulder abduction for only this amount of AROM:0-80 degrees. What MMT score would you give?
- 3+
- 2+
- 3
- 3-
Which of the following best describes a movement away from midline?
- Abduction
- Adduction
- Flexion
- Supination
The following are purposes of Kinesiology except:
- To understand bone structures and movement.
- To move safely.
- To move efficiently.
- To move effectively.
To keep up this site, we need your assistance. A little gift will help us alot.
Donate- The more you give the more you receive.
Related SubjectHealthcare Studies
Nursing Program
Life Science
Health Sciences
Diagnostic Cardiac Sonography
Diagnostic Medical Sonography
Biology
The Impact of Exercise on Blood Pressure
Physical Therapist Assistant
Personal Training
Health Education
Physical Education and Health Grade 12
Rhythmic Activities
Massage Therapy
Jake Paul: Social Media and Sports
Physical Education and Health Grade 11
How Wildlife Images Rehabilitation Operates
Justice Administration
Criminal Justice
Oleksandr Usyk: The Art of Boxing
Mike Brown: Basketball Coaching
Charlie Woods: Rising Star in Amateur Golf
Philadelphia Eagles Football Team
Mike Tyson: Boxing Legend
Dallas Mavericks Basketball Team
BMW M3 Performance and Engineering
Texas Tech Red Raiders Football Team
Honda CRX History and Legacy
Colorado Buffaloes Football Team
Abdullah Mason: Round of the Year
IShowSpeed vs. Noah Lyles
Dak Prescott: Leading the Cowboys
Physical Education and Health: Individual and Dual Sports
Physical Education and Health: Team Sports
Physical Science
Chemistry
Physics
Physics For Engineers
Calculus-Based Physics
Show All Subject
Affiliate Links
Shopee Cashback Voucher
Temu $0 Shipping Fee
Amazon 75% Off Discounts



